Key Instruments for RF & Microwave Signal Analysis
RF and microwave signals are a cornerstone of modern communication systems, from mobile networks and satellite links to radar and wireless devices. Testing these high-frequency signals requires specialized instruments that can capture, analyze, and characterize complex behavior that standard electronic test equipment simply can't handle.
If you're working in industries like telecommunications, aerospace, defense, or wireless product development, understanding the basics of RF and microwave testing is essential for ensuring performance, compliance, and system reliability.
What Makes RF Testing Different?
Unlike standard low-frequency electrical signals, RF and microwave signals operate in the MHz to GHz range. At these frequencies, signal behavior is influenced by many factors such as impedance mismatches, reflections, and electromagnetic interference that aren’t significant at lower frequencies.
This makes accurate testing more challenging and requires tools that are specifically designed to handle high-frequency signal paths, tight tolerances, and complex waveforms.
Common RF & Microwave Test Instruments
Here are some of the core instruments used in RF and microwave testing environments:
Spectrum Analyzers
These are essential tools for observing the frequency domain. They display signal amplitude over frequency, helping to identify and measure signal strength, spurious emissions, harmonic distortion, and noise. Spectrum analyzers are widely used for tasks like transmitter testing, EMI diagnostics, and interference analysis.
Shop Spectrum Analyzers on TTinstruments
Network Analyzers
Used to measure how RF signals behave when they encounter components like filters, antennas, and amplifiers. Network analyzers evaluate parameters such as gain, loss, and return loss (S-parameters), making them key for characterizing RF components and systems.
Shop Network Analyzers on TTinstruments
Signal Generators
These provide clean, stable RF signals for testing receivers and other devices. They allow precise control over frequency, power level, and modulation—helpful in evaluating performance across a device’s entire operating range.
Power Meters and Sensors
Used to measure absolute RF power with high accuracy. They're useful in both lab calibration and field testing settings, especially when working with transmitters or verifying system output levels.
Shop RF Power Meters and Sensors on TTinstruments
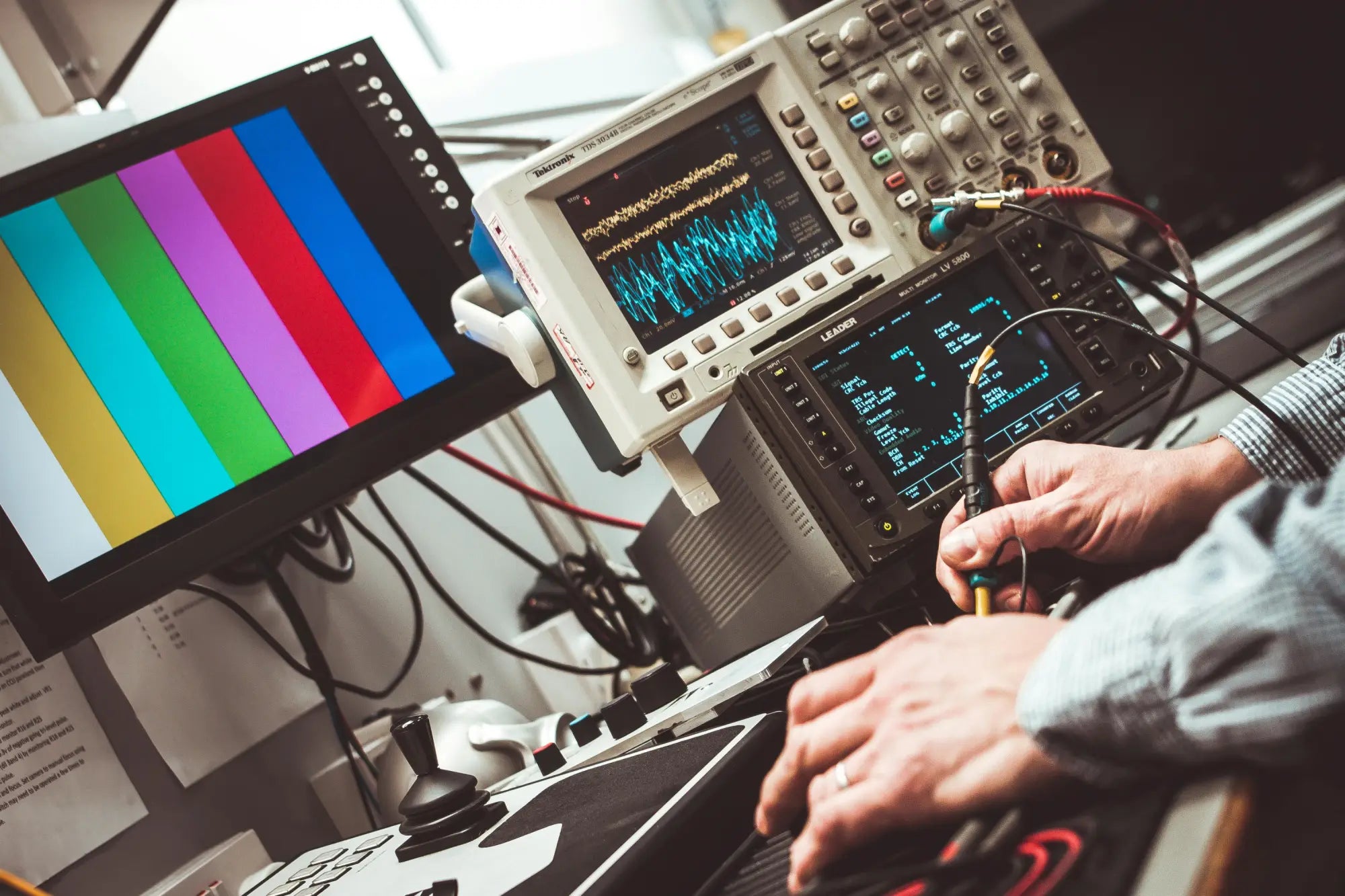
Oscilloscopes with RF Capabilities
While oscilloscopes are generally associated with lower-frequency applications, certain models and accessories enable them to visualize and decode RF-modulated signals, especially in time-domain analysis.
Shop RF-Ready Oscilloscopes and Accessories on TTinstruments
Factors That Affect Measurement Accuracy
High-frequency testing is sensitive, and many factors can impact the precision of your measurements:
-
Cable and connector quality: RF signals degrade quickly through poor interconnects. Use high-quality, low-loss cables and matched connectors.
-
Calibration: Regular calibration of instruments is crucial to maintain traceable accuracy, especially for network and spectrum analyzers.
-
Impedance matching: Most RF systems are designed for 50-ohm impedance. Mismatches can cause signal reflection, distortion, and measurement error.
-
Environmental conditions: RF performance can be affected by nearby interference, humidity, and temperature variations, particularly in field testing scenarios.
-
Test setup: Using proper shielding, grounding, and measurement techniques helps ensure repeatability and reliability.
Choosing the Right Equipment
When selecting RF and microwave test gear, consider:
-
Frequency range (does it match or exceed your test signals?)
-
Dynamic range and resolution
-
Portability vs. benchtop size
-
Modulation and decoding capabilities
-
Software support for automation or data logging
At TT Instruments, we offer a curated selection of RF and microwave test equipment for various applications. Whether you're looking for new or used spectrum analyzers, network analyzers, or signal generators, we ensure each unit is tested and ready for high-precision tasks.
Accurate RF and microwave measurements require the right combination of equipment, setup, and technique. By understanding the capabilities and applications of each instrument, you can create a reliable and efficient testing environment that meets the demands of high-frequency systems.
Browse our RF & Microwave collection at TT Instruments to find quality instruments designed to deliver performance and precision in even the most demanding environments.
Have Questions? Let's see if we can answer some of them below.
1. What is RF test equipment used for?
RF test equipment is used to measure, analyze, and simulate radio frequency signals, typically in the MHz to GHz range. It's essential for developing, testing, and maintaining wireless communication systems, radar, and RF components.
2. What’s the difference between a spectrum analyzer and a network analyzer?
A spectrum analyzer shows how signal power is distributed across frequencies, ideal for checking interference or signal purity. A network analyzer, on the other hand, measures how signals behave when passing through a device—useful for analyzing filters, amplifiers, and antennas.
3. Why is impedance matching important in RF testing?
Most RF systems are designed for 50-ohm impedance. A mismatch causes signal reflections, which can distort measurements and reduce power transfer efficiency. Proper matching ensures accurate, consistent results.
4. How often should RF test equipment be calibrated?
Calibration intervals vary by instrument and usage, but annual calibration is standard for most RF gear. Devices used in critical environments may require more frequent checks to maintain measurement integrity.
5. Can I use general-purpose oscilloscopes for RF signals?
Only to a limited extent. Standard oscilloscopes are not optimized for high-frequency RF signals. However, some advanced models with high bandwidth or RF-specific features can handle certain RF measurements.
6. What’s the ideal frequency range for my test equipment?
It depends on your application. Choose instruments with a frequency range that exceeds your highest test signal to allow headroom for harmonics, modulation, or future expansion.